
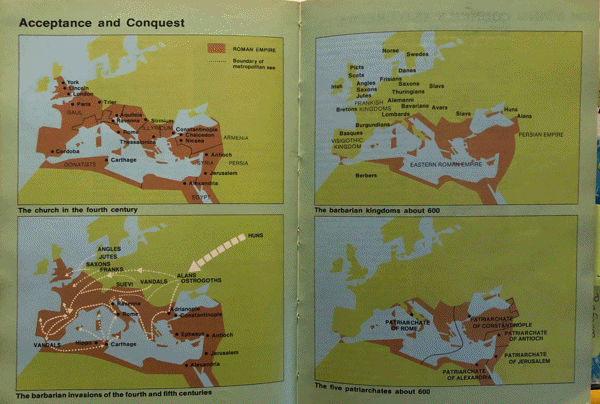


Primacy of Rome |
Bulgarian |
Filoque added to creed, pushing the Eastern Church further away |
4th Crusade depredations (1204) |
⇓ |
⇓ |
⇓ |
⇓ |
 1077 - Emperor Henry IV Before Pope Gregory VII
[20]
1077 - Emperor Henry IV Before Pope Gregory VII
[20]| PRO | CON |
| “Calvin must be reckoned as one of the greatest and best of men who God raised up in the history of Christianity.” Phillip Schaff “ | "We shall always find it hard to love the man who darkened the human soul with the most absurd and blasphemous conception of God in all the long and honored history of nonsense.” Will Durant |
 The Battle at the Gates of Vienna, September 12, 1683
[28]
The Battle at the Gates of Vienna, September 12, 1683
[28]